Let 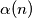 be the number of digits equal to one in the binary representation of a positive integer
be the number of digits equal to one in the binary representation of a positive integer 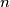 . Prove that:
. Prove that:
(a) the inequality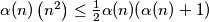 holds;
holds;
(b) the above inequality is an equality for infinitely many positive integers, and
(c) there exists a sequence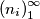 such that
such that 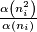
goes to zero as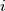 goes to
goes to 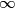 .
.
Alternative problem: Prove that there exists a sequence a sequence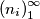 such that
such that 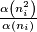
(d)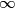 ;
;
(e) an arbitrary real number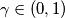 ;
;
(f) an arbitrary real number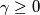 ;
;
as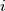 goes to
goes to 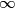 .
.
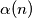 be the number of digits equal to one in the binary representation of a positive integer
be the number of digits equal to one in the binary representation of a positive integer 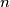 . Prove that:
. Prove that: (a) the inequality
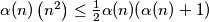 holds;
holds; (b) the above inequality is an equality for infinitely many positive integers, and
(c) there exists a sequence
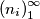 such that
such that 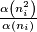
goes to zero as
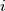 goes to
goes to 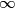 .
. Alternative problem: Prove that there exists a sequence a sequence
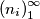 such that
such that 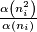
(d)
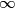 ;
;(e) an arbitrary real number
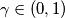 ;
; (f) an arbitrary real number
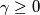 ;
; as
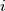 goes to
goes to 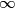 .
.  Školjka
Školjka